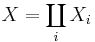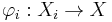Disjoint union (topology)
In general topology and related areas of mathematics, the disjoint union (also called the direct sum, free union, free sum, topological sum, or coproduct) of a family of topological spaces is a space formed by equipping the disjoint union of the underlying sets with a natural topology called the disjoint union topology. Roughly speaking, two or more spaces may be considered together, each looking as it would alone.
The name coproduct originates from the fact that the disjoint union is the categorical dual of the product space construction.
Contents |
Definition
Let {Xi : i ∈ I} be a family of topological spaces indexed by I. Let
be the disjoint union of the underlying sets. For each i in I, let
be the canonical injection (defined by  ). The disjoint union topology on X is defined as the finest topology on X for which the canonical injections are continuous (i.e. the final topology for the family of functions {φi}).
). The disjoint union topology on X is defined as the finest topology on X for which the canonical injections are continuous (i.e. the final topology for the family of functions {φi}).
Explicitly, the disjoint union topology can be described as follows. A subset U of X is open in X if and only if its preimage 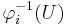 is open in Xi for each i ∈ I.
is open in Xi for each i ∈ I.
Yet another formulation is that a subset V of X is open relative to X iff its intersection with Xi is open relative to Xi for each i.
Properties
The disjoint union space X, together with the canonical injections, can be characterized by the following universal property: If Y is a topological space, and fi : Xi → Y is a continuous map for each i ∈ I, then there exists precisely one continuous map f : X → Y such that the following set of diagrams commute:
This shows that the disjoint union is the coproduct in the category of topological spaces. It follows from the above universal property that a map f : X → Y is continuous iff fi = f o φi is continuous for all i in I.
In addition to being continuous, the canonical injections φi : Xi → X are open and closed maps. It follows that the injections are topological embeddings so that each Xi may be canonically thought of as a subspace of X.
Examples
If each Xi is homeomorphic to a fixed space A, then the disjoint union X will be homeomorphic to A × I where I is given the discrete topology.
Preservation of topological properties
- every disjoint union of discrete spaces is discrete
- Separation
- every disjoint union of T0 spaces is T0
- every disjoint union of T1 spaces is T1
- every disjoint union of Hausdorff spaces is Hausdorff
- Connectedness
- the disjoint union of two or more nonempty topological spaces is disconnected
See also
- product topology, the dual construction
- subspace topology and its dual quotient topology
- topological union, a generalization to the case where the pieces are not disjoint